This blog post will guide you on troubleshooting Intune Endpoint Privilege Management. Recently I have setup and configure Intune Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) from scratch and demonstrated the end-user experience. In the demo, I used the example of the Microsoft 365 Apps for Enterprise setup file (OfficeSetup.exe) and provided just-in-time administrator access to the user to install the application.
This blog post goes a step further and provides troubleshooting tips for Intune Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM). To enable EPM on a client device, you need to create an elevation settings policy that also defines the default elevation response.
When a user requestes elevated access to a file using the right-click context menu option, Run with elevated access, EPM checks for any matching elevation rules policies for the file. If no corresponding rule is found, EPM falls back to the default elevation response set in the elevation settings policy. If a matching rule is found, elevation response set in the elevation rules policy will be applied on the file.
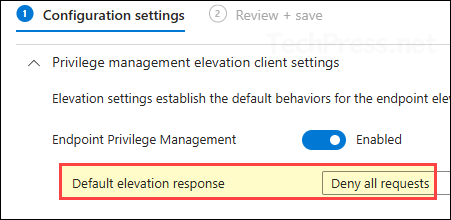
Elevation settings policy shown below sets the default elevation response to Deny all requests. Even if you set the default elevation response to Not configured, it will still default to Deny all requests. According to this policy, If you choose not to create an Elevation Rules policy, all EPM elevation requests for .exe, .msi, and .ps1 files will be automatically denied.
Contents
Microsoft Management Platform – Cloud (MMP-C)
Microsoft Management Platform – Cloud (MMP-C) is a cloud-hosted, Microsoft-managed platform that uses the Windows Declared Configuration (WinDC) protocol to deliver and maintain a device’s desired state. Its implemented on the devices as a linked enrollment (also referred to as dual enrollment) alongside standard MDM enrollment.
Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) and other Intune services leverage MMP-C to deliver configuration using a declarative model. This approach differs from the traditional OMA-URI–based method, where policies are only applied during Intune sync cycles. In the legacy model, if a policy changes, the device must wait until its next check-in with Intune servers to retrieve and apply the updated settings.
In contrast, the declarative approach allows the device to continuously evaluate its current configuration against the delivered configuration document. If any configuration drift is detected, the device can remediate itself automatically without waiting for the next check-in.
EPM was the first major feature delivered through MMP-C. It uses a linked enrollment and the WinDC protocol to establish this secondary configuration channel. The Advanced Device Inventory feature in Intune also utilizes MMP-C and the declarative model. Other Intune services are expected to adopt this modern platform over time. This architecture reduces network latency by enabling asynchronous, local policy evaluation and remediation, rather than relying on frequent communication with Intune servers.
Troubleshooting EPM: Perform Some Basic Checks First
Many times, issues can be resolved by making a simple change, often related to missing prerequisites. During my EPM setup, one of the devices was not enrolling into MMP-C, and the EPM agent was also failing to install, showing error code 214774989. As it turned out, the user had not been assigned the required Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) license. After assigning the license, the EPM agent installed successfully, and the device enrolled without any further issues.
- EPM license: Ensure that users are assigned Microsoft Intune suite or Microsoft Intune Endpoint Privilege management add-on license. Without this, EPM settings policy will not be applied.
- OS Version: If you deploy EPM policies to a device with incompatible OS version. Intune will show the status of the policy as Not applicable for the device. Compatible OS version list.
- OS Architecture: EPM is only compatible with 64-bit version of OS, including Arm64 devices.
- Connectivity: Ensure that the device is able to reach EPM cloud endpoints. If your organization uses a firewall, make sure that it allows port tcp/443 port for cloud domains: *.dm.microsoft.com and *.events.data.microsoft.com. For more info: EPM networking requirements.
- User Account Control (UAC): If your organization has User Account Control (UAC) disabled, you may experience issues when using Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM).
- App control for business (ACfB): If you are using App Control for Business (ACfB), ensure that EPM executables are allowed to run. Else, EPM agent will not be installed.
- Applocker: Similar to ACfB application control policies, ensure that Applocker policies are not blocking EPM Agent installation.
- Group Policies: Ensure that there are no Group policies blocking installation of apps which could block the installation of EPM agent.
- Files downloaded from Internet: If you have downloaded setup files from the internet, ensure they are unblocked using file properties. Only unblock files that you trust. If a file is blocked, EPM will throw an error. Unable to elevate this app because it came from the Internet or another computer. Error code (0x87E00206) (-2015362554).
- Workplace join devices: Workplace join type of devices are not supported by EPM.
- Elevating a file from Network Share: If you try to elevate a file located on a network share, it will not work, as EPM only supports elevation for files stored locally on the device.
- Azure Virtual Desktop: As of now, EPM solution is not supported on Azure virtual desktop (AVD).
- EXE, MSI and PS1: Only .exe, .msi and .ps1 file extensions are supported by EPM.
Verify Elevation Settings Policy on Client Device
After you create and deploy an Elevation Settings policy to enable Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) on a client device, the device performs a dual enrollment: it remains enrolled in the standard Intune MDM channel and establishes a secondary enrollment with Microsoft Management Platform – Cloud (MMP-C). In the following sections of this post, I will show you how to verify this dual enrollment, which can help when investigating EPM enrollment-related issues.
Dual Enrollment (MMP-C)
Intune EPM requires a secondary MDM enrollment to the Microsoft Managed Platform (MMP-C) service. Use any of the below methods to verify whether dual enrollment has been successfully completed on the client device.
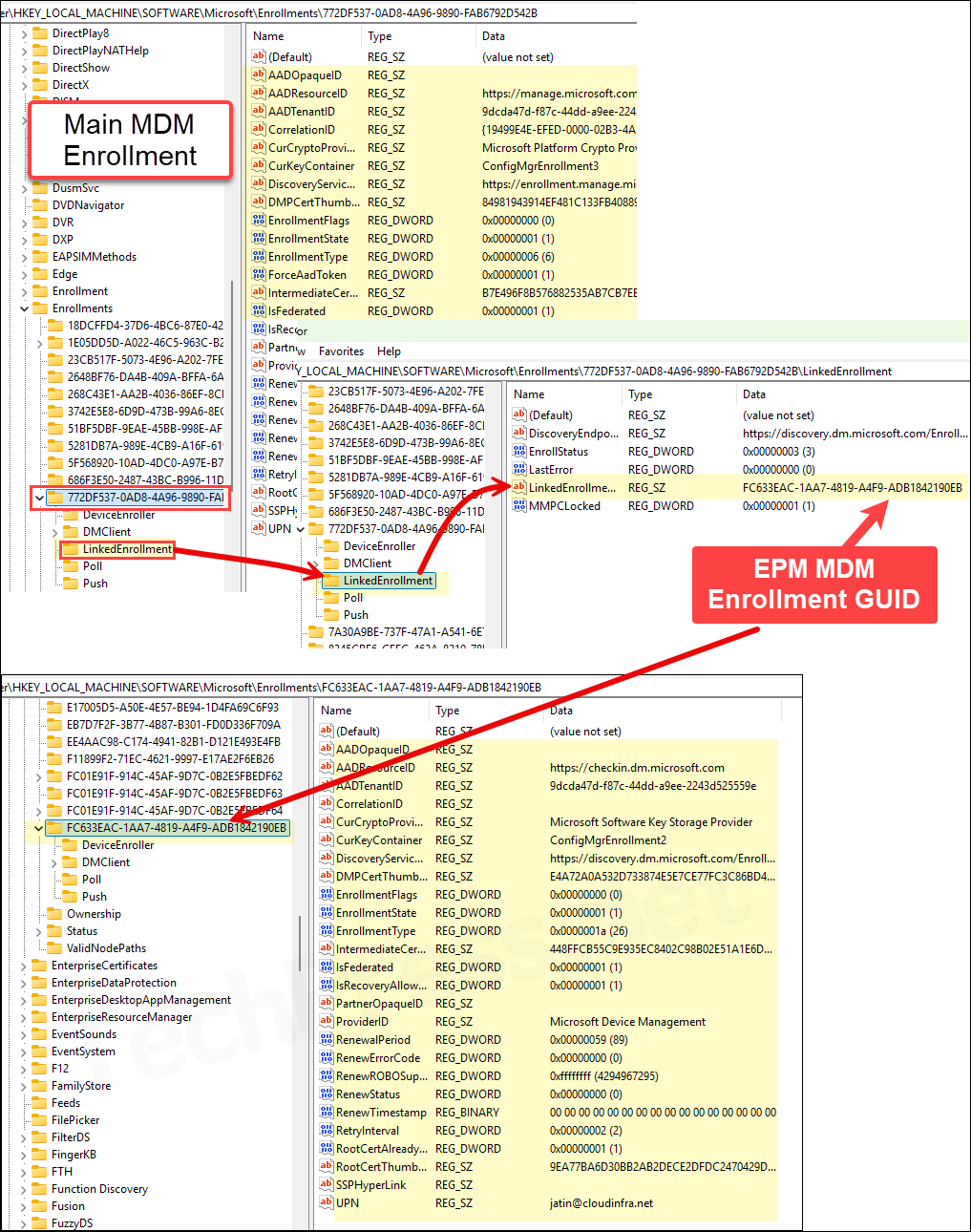
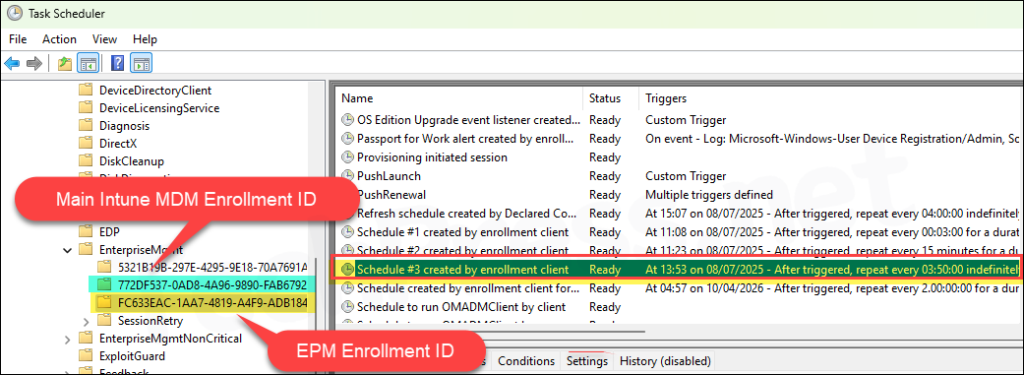
- Registry Check: Device initiates a dual enrollment with Intune Microsoft Managed Platform Cloud (MMP-C). You can verify this dual MDM enrollment by checking the following registry path: HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\Microsoft\Enrollments. Locate the primary MDM enrollment ID in the list of registry keys under Enrollments, then navigate to the LinkedEnrollment folder. There, you should find the LinkedEnrollmentId associated with MMP-C. If it’s missing, the device is not linked to the EPM service. Notice the DiscoveryEndpoint registry entry is set to https://discovery.dm.microsoft.com/EnrollmentConfiguration?api-version=1.0.
If you check the Main MDM Enrollment registry key, you will find the DiscoveryServiceFullURL reg entry is set to https://enrollment.manage.microsoft.com/enrollmentserver/discovery.svc and If you open the linked enrollment GUID registry key, you will find that the DiscoveryServiceFullURL is set to DiscoveryServiceFullURL https://discovery.dm.microsoft.com/EnrollmentConfiguration?api-version=1.0. Its a MMP-C enrollment discovery endpoint.
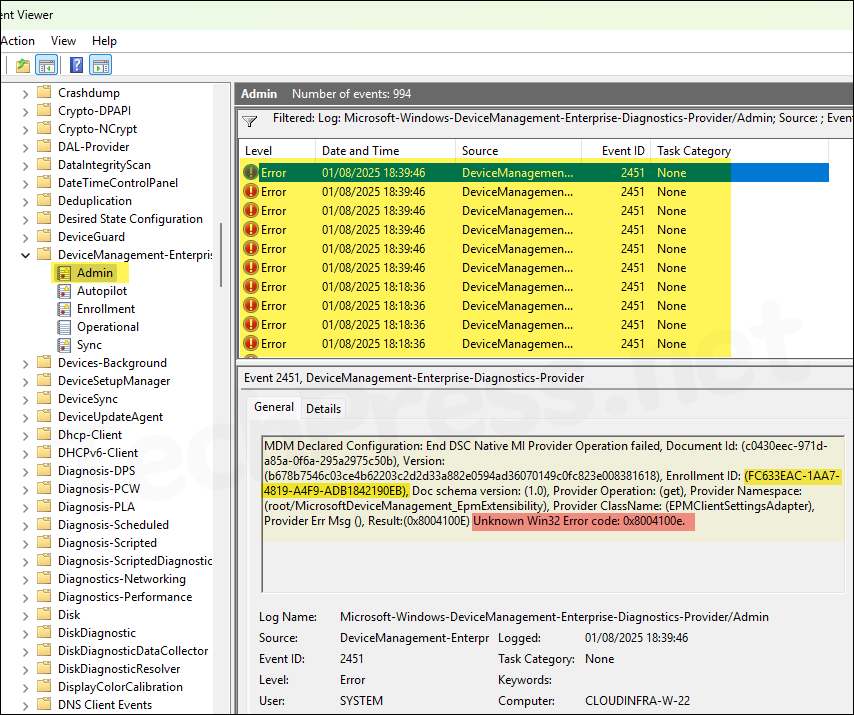
- Event viewer Check: Use Event Viewer to confirm the dual enrollment. If there are any issues, you will be able to find it in the event logs. Launch Event viewer > Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > DeviceManagement-Enterprise-Diagnostics-Provider > Admin. Filter using the event ID 2451 which shows if there are any errors/issues.
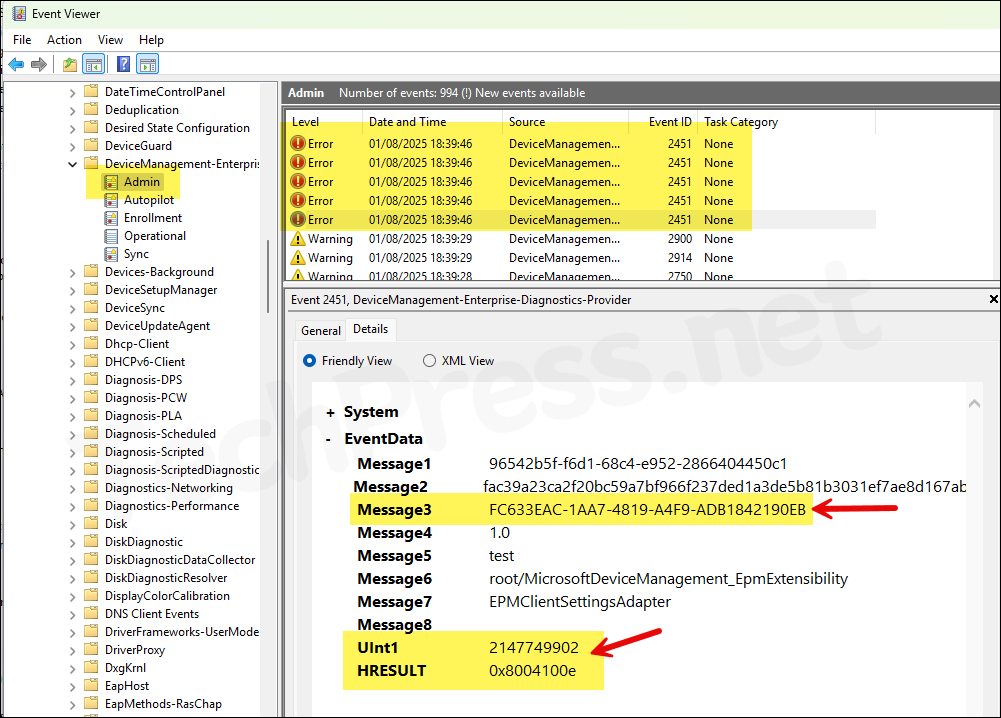
I got a lot of errors in the event viewer which are related to the EPM. The error message itself is not very descriptive, but it does reference the EPM enrollment ID: FC633EAC-1AA7-4819-A4F9-ADB1842190EB in the log and shows Unknown Win32 Error code: 0x8004100e. This points towards a potential issue with the EPM enrollment or EPM Agent Installation related issues.
MDM Declared Configuration: End DSC Native MI Provider Operation failed, Document Id: (c0430eec-971d-a85a-0f6a-295a2975c50b), Version: (b678b7546c03ce4b62203c2d2d33a882e0594ad36070149c0fc823e008381618), Enrollment ID: (FC633EAC-1AA7-4819-A4F9-ADB1842190EB), Doc schema version: (1.0), Provider Operation: (get), Provider Namespace: (root/MicrosoftDeviceManagement_EpmExtensibility), Provider ClassName: (EPMClientSettingsAdapter), Provider Err Msg (), Result:(0x8004100E) Unknown Win32 Error code: 0x8004100e.
UPDATE: After investigating this error, I discovered that App Control for Business (WDAC) was preventing EPM from being enabled and blocking the installation of the EPM agent. If you are also using App Control for Business in your environment, you’ll need to create rules to whitelist the EPM agent and its components. In my test lab, I temporarily switched App Control for Business to Audit mode, which allowed the EPM Agent to install successfully. You could also create supplemental rules to whitelist EPM and keep the App control for business Enforce mode.
- Task Scheduler Check: Open Task Scheduler (as admin) and navigate to Microsoft > Windows > EnterpriseMgmt. You’ll see a folder named with the Intune enrollment GUID (with tasks like Schedule #3 every 8 hours). There should be a second folder named with the EPM GUID, containing its own tasks (Schedule #3 running ~every 3:50:00 hours). The presence of these tasks confirms the dual enrollment. If the second set of tasks is does not exist, EPM policies never fully enrolled.
EPM Agent Installation and Services
After you deploy elevation settings policy to enable EPM on the client device, it automatically installs EPM agent on the device. The role of the agent is to enforce EPM policies, handling of MMP-C communication, install a shell extension which provides Run with elevated access option in file explorer etc.
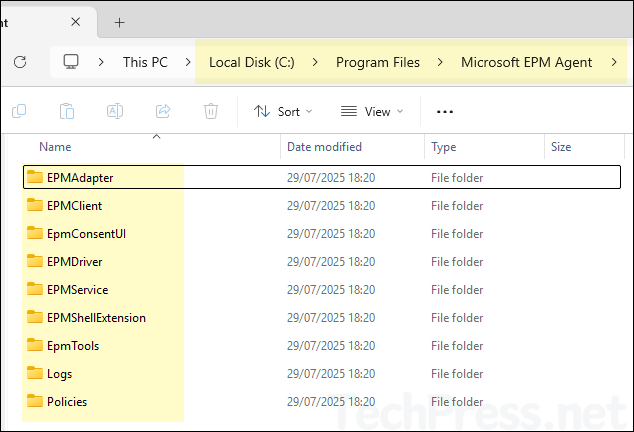
Install Location of EPM Agent
- Check and confirm whether the folder C:\Program Files\Microsoft EPM Agent\ exists. Highlighting some of the main folders which can be useful for troubleshooting are:
- EpmTools: Contains the
EpmCmdlets.dllPowerShell module for troubleshooting. - Logs: Contains EPM service and agent logs.
- Policies: Stores the Elevation Settings and Elevation Rules in
.datfile format. - EPMShellExtension: Contains the MSIX package and supporting files that enable the Run with elevated access option in File Explorer’s context menu.
- EpmTools: Contains the
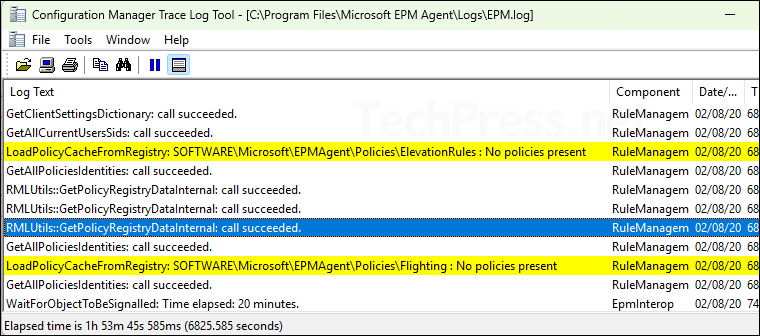
- Below is a screenshot of C:\Program Files\Microsoft EPM Agent\Logs\EPM.log file.
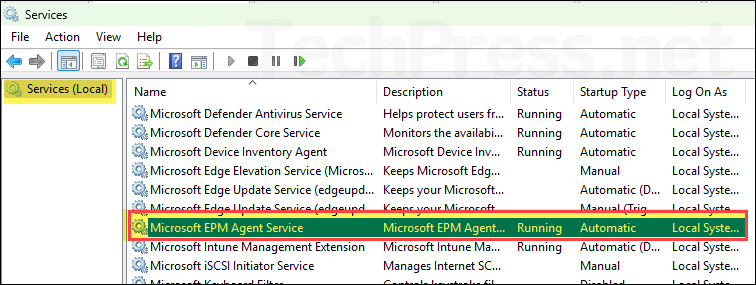
Microsoft EPM Agent Service
EPM agent runs a Windows service called Microsoft EPM Agent Service. Its default Startup type is Automatic and runs using Local System account. Ensure that it’s in Running state. The service is located in C:\Program Files\Microsoft EPM Agent\EPMService\EpmService.exe folder.
EPM Agent Installation Issues
If you encounter issues installing the EPM agent on a device, you can follow below troubleshooting steps to help identify and resolve the problem:
- Event logs: When EPM agent is not installing on your device, the first step is to check the event viewer, which can point you in the right direction. Event viewer > Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > DeviceManagement-Enterprise-Diagnostics-Provider > Admin. Filter the logs using error code: 2147749902 or 0x8004100e. The event ID for this error event would be 2451. Notice the EPM enrollment ID and related error codes in below screenshot.
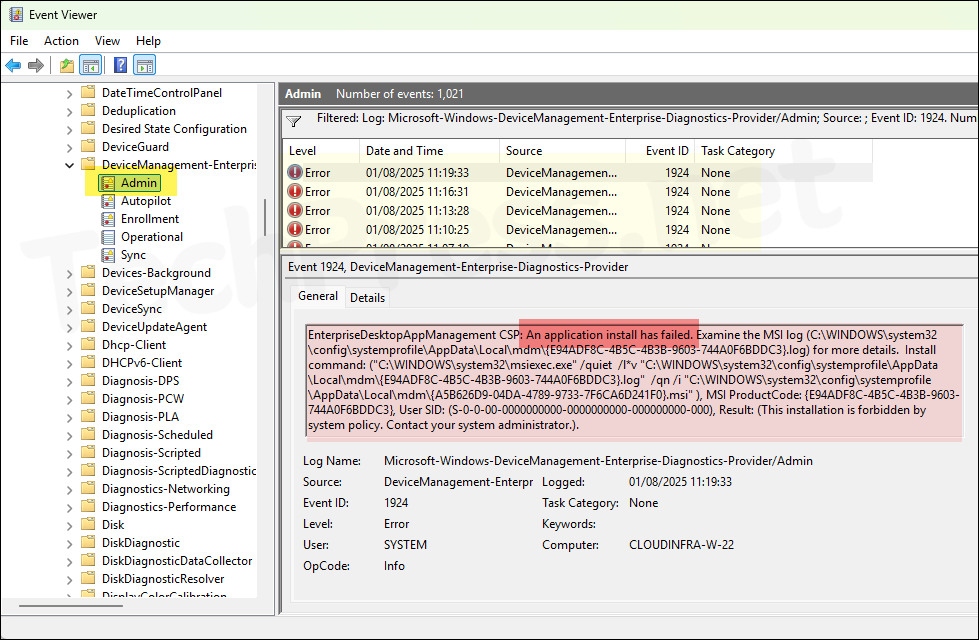
- Filter the event log using Event ID: 1924. You will find more information about EPM agent installation issue. The error message says that the Installtion is forbidden by system policy.
EnterpriseDesktopAppManagement CSP: An application install has failed. Examine the MSI log (C:\WINDOWS\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\mdm{E94ADF8C-4B5C-4B3B-9603-744A0F6BDDC3}.log) for more details. Install command: (“C:\WINDOWS\system32\msiexec.exe” /quiet /l*v “C:\WINDOWS\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\mdm{E94ADF8C-4B5C-4B3B-9603-744A0F6BDDC3}.log” /qn /i “C:\WINDOWS\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\mdm{A5B626D9-04DA-4789-9733-7F6CA6D241F0}.msi” ), MSI ProductCode: {E94ADF8C-4B5C-4B3B-9603-744A0F6BDDC3}, User SID: (S-0-0-00-0000000000-0000000000-000000000-000), Result: (This installation is forbidden by system policy. Contact your system administrator.).
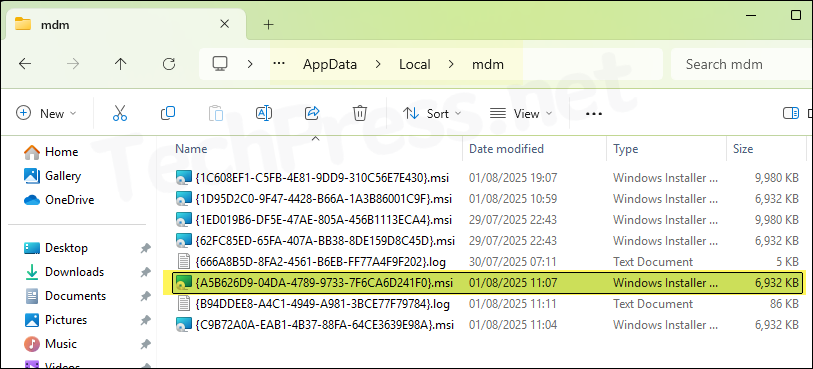
- To get the EPM Agent MSI file, you first need to find the GUID of the MSI file from event viewer log and then browse to the folder: C:\Windows\System32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\mdm.
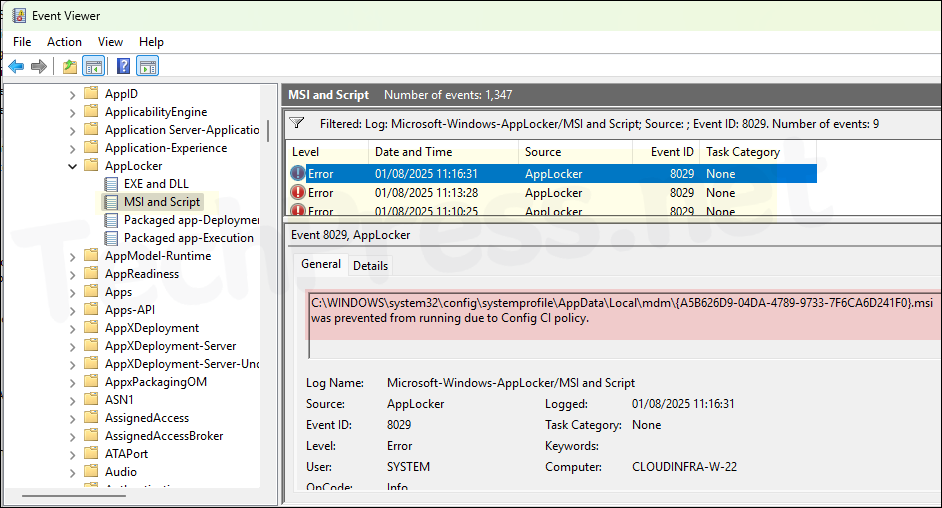
- Launch Event viewer > Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > AppLocker > MSI and Script. Filter the event log using event id 8029 and scroll through the list to find the GUID for EPM MSI file. Below error suggests that the MSI was prevented running due to config CI policy.
C:\WINDOWS\system32\config\systemprofile\AppData\Local\mdm{A5B626D9-04DA-4789-9733-7F6CA6D241F0}.msi was prevented from running due to Config CI policy.
- To check further information on the EPM agent installation error. Launch Event viewer > Applications and Services Logs > Microsoft > Windows > CodeIntegrity > Operational. Filter the event log using event id 3004. Find more information about this event ID here:
Windows is unable to verify the image integrity of the file \Device\HarddiskVolume3\Program Files\Microsoft EPM Agent\EPMAdapter\EpmAdapter.dll because file hash could not be found on the system. A recent hardware or software change might have installed a file that is signed incorrectly or damaged, or that might be malicious software from an unknown source.
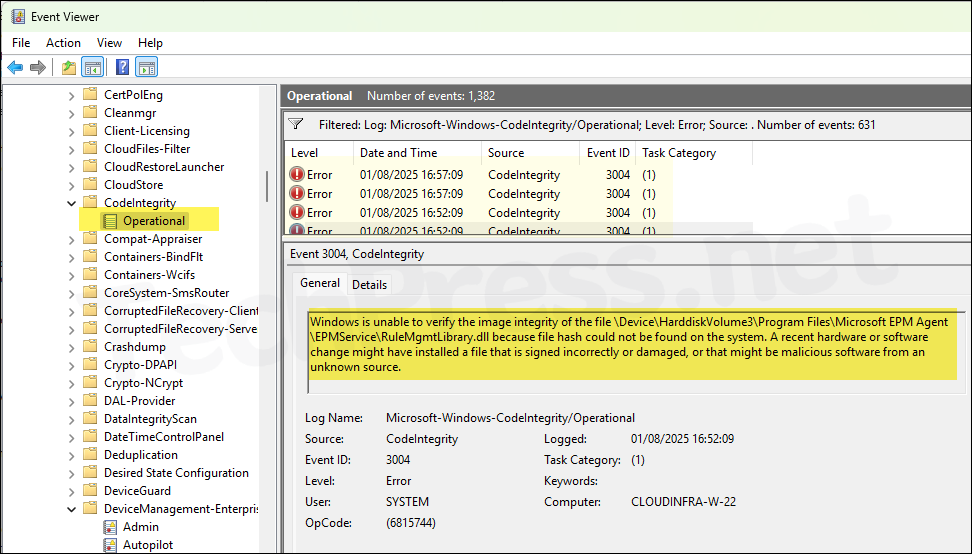
I had recently enabled App control for business (ACfB) on the devices and I investigated in that direction, changed ACfB policies from enforced mode to audit mode to test. After rebooting the device and waiting for few minutes, EPM agent got installed successfully. It confirmed that the issue was because of AcfB policies.
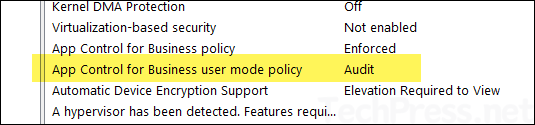
To fix EPM Agent Installation issues, ensure that the EPM agent MSI is not being blocked by any application control policies, such as AppLocker or App Control for Business. Also, check if any third-party security tools might be preventing the installation. If you’re using EPM in an Entra hybrid join scenario, review your Group Policy settings for any rules that may block the agent.
If you have to keep ACfB in enforced mode, you would have to create a supplemental policy using App Control for Business Wizard and create an allow rule for EPM agent MSI. GUID could be different so use agent’s certificate, publisher and other unique information while creating a supplemental rule. Deploy the rule and try again.
In rare cases where you need to remove or uninstall the EPM agent from a device, you can use below PowerShell command:
Uninstall EPM Agent
Get-WmiObject Win32_Product | Where-Object Name -like "EPM Agent" | ForEach-Object { $_.Uninstall() }Run with Elevated Access in Right-Click Context menu
If you find that the EPM agent has been installed successfully but the right-click context menu item Run with elevated access is not appearing. Investigate using below steps:
- Verify the existence of the file C:\Program Files\Microsoft EPM Agent\EPMShellExtension\EpmShellExtension.msix. If the file is present, review the Event Viewer logs (as detailed above) to identify any related errors. It’s possible that a program, rule, or policy is blocking the installation of MSIX files. Try installing the .msix file manually to check whether it installs successfully or if any errors occur.
- Start menu and taskbar: Applications pinned to the taskbar or Start menu may not show the Run with elevated access context menu. This is a known limitation. To compare the behavior, try right-clicking the same application directly from File Explorer, where the option should appear if EPM is configured correctly.
EPM Powershell Module (EpmTools)
Once the EPM agent is installed on your device, it also installs EPM Powershell module under EpmTools folder. PowerShell module location: C:\Program Files\Microsoft EPM Agent\EpmTools. Use the module to check and confirm if EPM is enabled on your device, elevation rules and client settings etc.
- Launch PowerShell console (as administrator) on your device where EPM agent is installed and execute below commands:
Import EPM PowerShell module
Import-Module "C:\Program Files\Microsoft EPM Agent\EpmTools\EpmCmdlets.dll"List all commands available in EpmCmdlets.dll module
Get-Command -Module EpmCmdlets | Select-Object Name, CommandType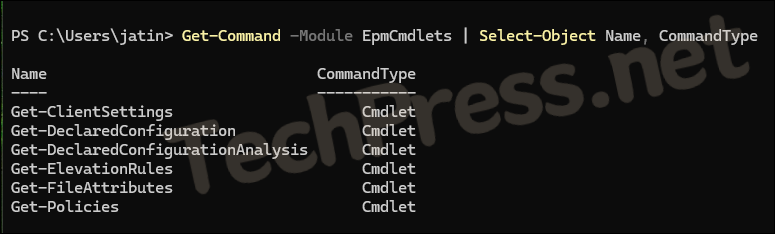
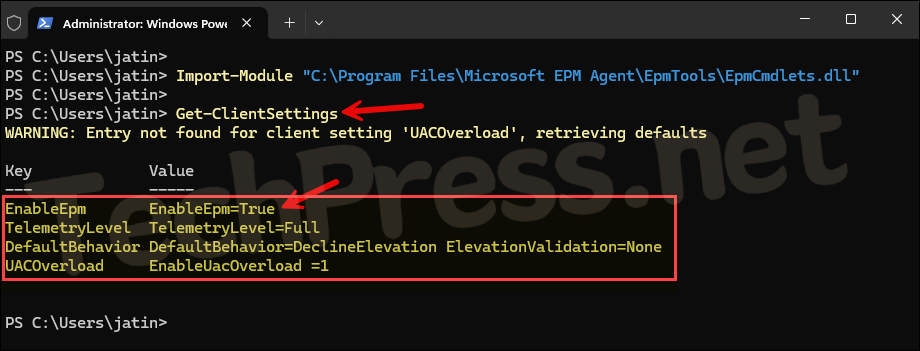
- Get-ClientSettings: It shows the effective EPM settings on the client. The settings you configure in EPM settings policy can be confirmed using this cmdlet.
EPM Settings Policy Status
Get-ClientSettingsKey Value
--- -----
EnableEpm EnableEpm=True
TelemetryLevel TelemetryLevel=Full
DefaultBehavior DefaultBehavior=DeclineElevation ElevationValidation=None
UACOverload EnableUacOverload =1
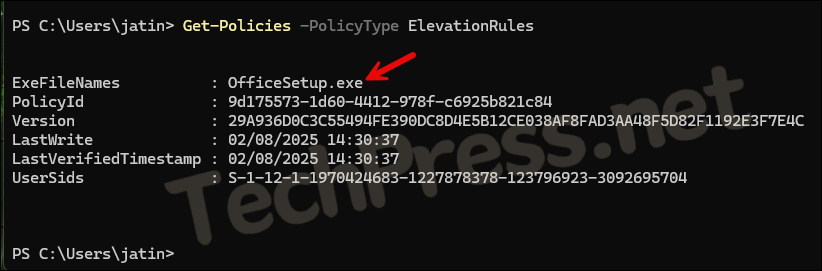
- Below command provides the list of elevation rules policies applied on a device. If you have deployed elevation rules policies and you don’t see it here, it could be an Intune sync or OS compatibility issue.
Get Elevation Rules Policies
Get-Policies -PolicyType ElevationRulesExeFileNames : OfficeSetup.exe
PolicyId : 9d175573-1d60-4412-978f-c6925b821c84
Version : 29A936D0C3C55494FE390DC8D4E5B12CE038AF8FAD3AA48F5D82F1192E3F7E4C
LastWrite : 02/08/2025 14:30:37
LastVerifiedTimestamp : 02/08/2025 14:30:37
UserSids : S-1-12-1-1970424683-1227878378-123796923-3092695704
- Get-DeclaredConfiguration: Lists all raw declared configuration documents in JSON format.
- Get-DeclaredConfigurationAnalysis: Shows each policy document and if it has been processed by EPM.
- Get-FileAttributes: Extracts File attributes (e.g., file hash, product name, publisher) used to define elevation rules. Example: Get-FileAttributes -FilePath “C:\Temp\OfficeSetup.exe”.
- Get-ElevationRules: Use this cmdlet to query the rules available on the device.
Troubleshooting EPM using Intune admin center
Even though you can gather a lot of information for troubleshooting EPM-related issues directly from the client device, you can also sign in to the Intune admin center to perform additional checks and ensure that Endpoint Privilege Management (EPM) is functioning as expected.
Error code 214774989
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Endpoint Privilege Management > Policies.
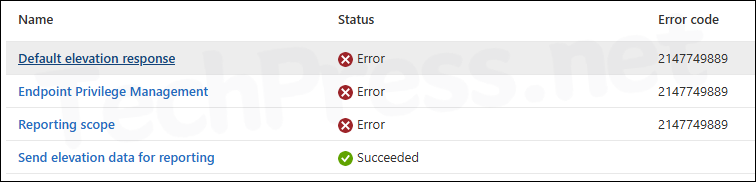
- Click on the Elevation Settings policy to check its status. Then, click on the View report button to get more detailed information. Select the device showing an error to investigate the issue further.
As shown in the below screenshot, I’m seeing an error code 214774989 corresponding to each setting configured in the Elevation Settings policy. This shows that EPM was not successfully enabled on the device.
Check-in status showing Not applicable
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Endpoint Privilege Management > Policies.
- Click on the Elevation Settings policy to check its status. Then, click on the View report button to get more detailed information. You may find that there are devices where the check-in status is showing as Not applicable. This could be due to the unsupported version of Operating system (OS), unsupported OS architecture (like 32-bit).
EPM Reports
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Endpoint Privilege Management > Reports. This section provides reporting for managed and unmanaged elevations. Go through the data to troubleshoot issues related to elevation requests.
EPM Policy Conflict
- Elevation Settings policy: If you apply multiple elevation settings policy to the same device with conflicting policies, resultant policy will be to enable EPM on the device until the conflict is cleared.
- Elevation rules policy: If you create two elevation settings rules for the same application and apply it to the same device, then below action takes place:
- Deny rule take precedence over allow rule.
- If one rule is deployed to the user and other one is deployed to device, the one applied to user will take priority.
- Run with file hash will win, if no hash provided, rule with most file attributes will win.
- If there is still conflict, then rule will win in based on elevation behavior in order: User confirmed, Support Approved and then Automatic rule.
Elevation Request (Support-Approved)
- To approve any pending elevation requests, Sign in to the Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Endpoint Privilege Management > Elevation requests tab. As of now, notifications are not sent to the administrators for elevation requests. Elevation requests tab will show all pending elevation requests.
- Users requeting support approval for elevation must be the primary user on their device, else Intune will not accept the elevation request. To check the Primary user of a device, Sign in to the Intune admin center > Devices > All devices > Click on any device to find out the Primary user information.
Microsoft is working on updating EPM to allow non-primary users to initiate support approval requests.
- Once administrator approved the elevation request, user will get a toast notification on their device confirming that the request has been approved and they can run the application as administrator.
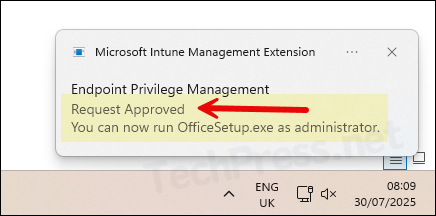
- User will get administrator rights for the approved application only for 24 hours. If you want to revoke the admin rights, you can go back to the elevation requests and click Revoke button.
- If Administrator denies the elevation request, the user will not receive an automatic notification. However, the administrator can manually send an email to inform the user about the denied request. If you are using an internal service management tool such as ServiceNow, updating the related incident or request typically triggers an automated email notification to the user.
Additional Troubleshooting Steps
- Check Intune logs: You can check Intune logs to determine if there are any issues with the Intune Management Extension agent itself. These logs are located at: C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension\Logs\ on the client computer. You can either sign in to the client device to review the logs locally or collect them remotely through the Intune admin center.
- Intune Service Outage: Rarely, Intune might have an outage or delay. Check the M365 Service Health for Intune if widespread policy delivery issues occur. EPM being a newer feature might not explicitly show, but a general Intune issue could affect it.
- PowerShell scripts: You can also create a PowerShell script:
- To query the Intune enrollment registry key HKLM\Software\Microsoft\Enrollments\{GUID}\LinkedEnrollment and check the status of EnrollStatus, LastError, LinkedEnrollmentID, MMPCLocked reg entries.
- Checks if the EPM service is running,
- Execute
Get-ClientSettingsand get check EnableEpm Status.
Diagnostic Logs
- Collect Intune logs: As discussed earlier, Use Intune’s remote diagnostics feature to gather logs from the device without user intervention.
- EPM logs: You may manually collect the EPM agent logs by asking the user to zip the C:\Program Files\Microsoft EPM Agent\Logs folder. These logs don’t contain sensitive info beyond computer/usernames and file paths, so they can be reviewed to pinpoint issues as discussed.
EPM Elevation Errors
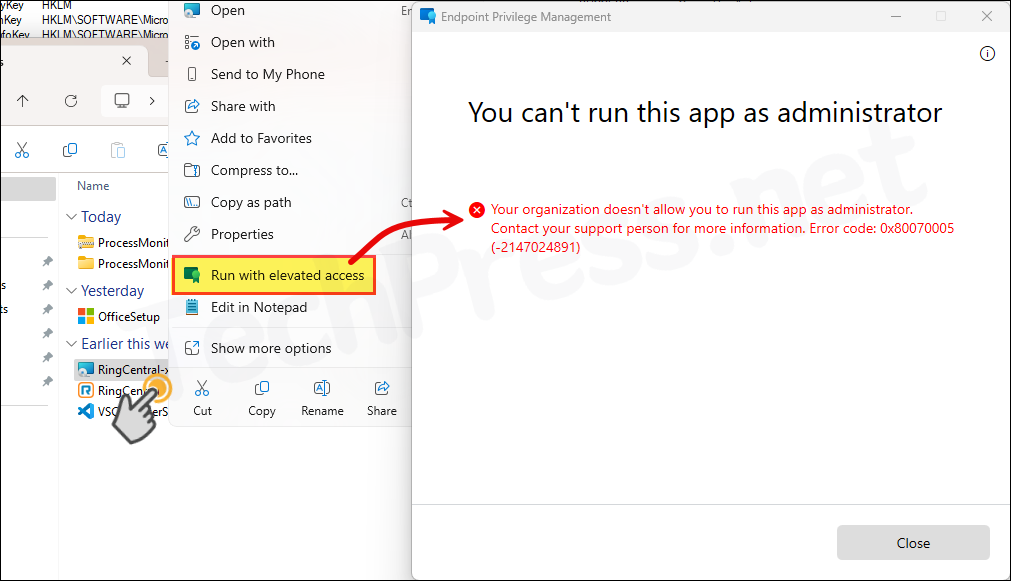
When an EXE, MSI, or PS1 file is executed and no matching elevation rule policy exists for it, the default elevation response configured in the Elevation Settings policy will be applied. Below error is a result of an elevation request for a file which is not allowed by EPM.
Your organization doesn’t allow you to run this app as administrator. Contact your support person for more information. Error code: 0x80070005 (-2147024891)