In this post, I will show you how to set macOS device name to serial number using Intune. By default, macOS derives the device name from the first user’s full name and the Mac model. For example, I have a device enrolled in Intune named Cloudinfra MacBook Pro. In this name, Cloudinfra reflects the first user’s full name and MacBook Pro is the model.
In an organization, you should enforce a standard, unique naming convention for all managed macOS devices. I will recommend creating a standard naming structure for Intune registered/joined Mac devices. This is a similar experience when you apply a device naming template for Windows devices using %SERIAL% macro.
Contents
Manually Rename Mac to Serial Number in Intune
You can manually rename an Intune enrolled Mac device to serial number using Intune Portal. You first need to get the serial number of the device and then perform rename operation. Let’s check the steps:
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Devices > macOS > click on the device you want to rename.
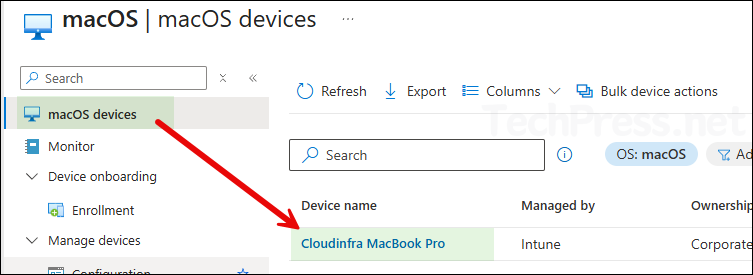
- From Overview page, copy the serial number of Mac.
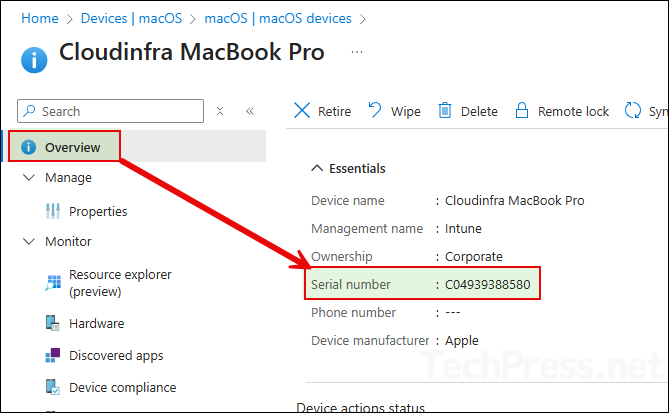
- Go to the Properties page, select Rename, and paste the Mac device’s serial number. Then click Rename again to apply the change.

Rename Mac Device Name to Serial Number Using a Shell Script
In the previous section, we have seen how to manually rename a macOS device via Intune admin center. This is easy and can be done in few steps. However, what if you have to rename 100’s of Mac devices. This will take a lot of time to perform this change manually and therefore not a recommended method. Deploy a shell script via Intune to rename Mac devices in bulk.
Microsoft has provided shell scripts in their GitHub repository that can rename multiple macOS devices to their serial number at scale. There are two scripts available for download, DeviceRename.sh and DeviceRename2.sh. Both the scripts have different device naming templates and apply to Apple business manager devices.
Therefore, I have created a modified version of the script DeviceRenametoSerial.sh, which has a device naming template to rename the device to just the serial number. It also has a toggle switch for Apple business manager, BYOD or all devices. Go through below points to get more details about all these scripts and decide on which one to use.
- DeviceRename.sh: This script will apply a device naming template of $OwnerPrefix-$ModelCode-$SerialNum-$Country. For example: CO-MBA-C02BA222DC-US. Additionally, it will also check if a device is enrolled using Apple business manager (ABM) and if a device is not enrolled via ABM, it will not be renamed.

- DeviceRename2.sh: This script will apply a device naming template of
$CountryCode-$SerialNum. Additionally, it will also check if a device is enrolled using Apple business manager (ABM) and if a device is not enrolled via ABM, it will not be renamed.

- DeviceRenametoSerial.sh: This one is the modified version of the previous scripts to meet the requirements of effectively setting macOS device name to its serial number. The script supports both Apple business manager and BYOD devices. There is a toggle switch at the top (TARGET_SCOPE) of the script, use it to target either ABM, BYOD or all devices. The script can be downloaded from my GitHub repository: DeviceRenametoSerial.sh · GitHub. In the next step, I will use this script which meets our requirements and deploy it to Mac devices via Intune.

Deploy DeviceRenametoSerial.sh Shell Script via Intune
Download DeviceRenametoSerial.sh script to rename Mac devices to their serial numbers and deploy it via Intune. You can also use the other two scripts as needed for your use case.
- Sign in to the Intune Admin Center > Navigate to Devices > macOS > Scripts > Click Add.
- Basics tab: Provide a name and description of the script deployment. For example: Rename Mac Device to Serial Number.
- Script settings: Click the blue folder icon and select the DeviceRenameToSerial.sh script. Configure below script settings for this deployment.
- Run script as signed-in user: No
- Hide script notifications on devices: Yes
- Script frequency: Every 1 week
- Max number of times to retry if script fails: 3

- Scope tags (optional): A scope tag in Intune is an RBAC label you add to resources (policies, apps, devices) to limit which admins can see and manage them. For more Information, read: How to use Scope tags in Intune.
- Assignments: Assign the script to Entra security groups that contain the target users or devices. As a best practice, pilot with a small set first; once validated, roll it out more broadly. For guidance on assignment strategy, see Intune assignments: User groups vs. Device groups.
- Review + add: Review the deployment summary and click Add.
Sync Intune Policies
The device check-in process might not begin immediately. If you’re testing this policy on a test device, you can manually kickstart Intune sync from the device itself or remotely through the Intune admin center.
Alternatively, you can use PowerShell to force the Intune sync on Windows devices. Restarting the device is another way to trigger the Intune device check-in process.
Monitor Deployment Progress
To monitor app deployment, access the Intune admin center. Navigate to Devices > macOS > Scripts. Click on a shell script to check its status, then go to the Overview page to view the shell script deployment status.
To check the deployment status on a per-device or per-user basis, select Device status or User status under the Monitor section.

Shell Script Deployment Status
| Script Status | About the Result |
|---|---|
| Success | Shell script execution was successful. Script returned Zero (0) exit code. |
| Failed | Shell script execution was not successful. Script returned a Non-Zero exit code. |
| No Status | If the device is offline, No status can be reported to Intune until the device is back Online. Therefore, in that case, Intune will show as No Status. |
End User Experience
To speed up the deployment of this script, I have clicked Check status in the Company portal app and device rename operation completed within few minutes. Let’s check the status of the device, and then we will check the device status on Intune admin center.
- Sign in to one of the target Mac device and open System settings > General > About to check and confirm if the device has been renamed to serial number.

- Open the Company Portal app and confirm if the device is now renamed to serial number.

- Sign in to the Intune Admin Center > Navigate to Devices > macOS > macOS devices. Check and confirm if the target devices are now renamed to serial number.

Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues deploying the shell script, use the troubleshooting steps below to identify the root cause.
Shell Scripts Not Running on Target macOS Devices
Even if you have successfully tested the shell script manually before creating the deployment in the Intune admin center, it may still fail to run on some target macOS devices. Below are a few reasons the shell script might fail to execute:
- If you recently created the Script deployment, you may need to wait for the Intune device check-in process to complete. For more information about the Intune device check-in process on Mac devices, refer to the article: Force Intune Sync on macOS devices. The default device check-in happens every 8 hours.
- Ensure the target device is online and connected to the Internet for successful MDM agent check-in. If the device is online, you can ask the user to open the Company Portal app on their device and Initiate Device check-in once.
- Ensure that the Intune agent is installed on the target Mac device. Intune agent is installed at the location /Library/Intune/Microsoft Intune Agent.app. Check if Microsoft Intune agent.app exists.
- Review Intune logs on macOS devices. To collect and investigate the logs, refer to the step-by-step guide on log collection: How to Collect Intune Logs from macOS Devices.
- If there are issues with the Intune agent, it typically recovers within 24 hours. Allow time for it to move from an unhealthy to a healthy state. If problems persist after 24 hours, raise a support ticket with Microsoft.
