In this blog post, I will show you how to troubleshoot Volume Shadow Copies (VSS) on Windows. Volume shadow copy service (VSS) was introduced with Windows server 2003 to facilitate the coordination between different backup components which are required to backup the application data in a consistent state without taking the application offline.
VSS helps create a consistent point-in-time copy or snapshot of the data for backup. One of the example of an application which utilize VSS for backing up data is Windows server backup.
There are 4 main components of VSS: VSS service, VSS requester, VSS writer and VSS provider. For more information about these components and how VSS works, please refer to the link: #how-vss-works.
In this blog post, we will focus on different commands to manage VSS and troubleshoot errors and issues related to VSS.
Contents
1. Vssadmin command
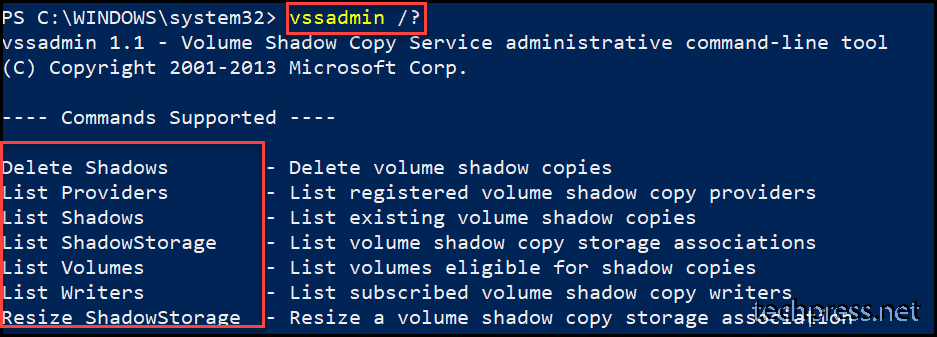
vssadmin is a built-in command-line tool on Windows devices for troubleshooting issues related to VSS. It shows current volume shadow copy backups and all shadow copy writers and providers installed on the system. It offers various switches for managing vss and fixing related issues.
Open command prompt or PowerShell console on your device and run vssadmin /? command to list different switches.
| Command | Description | Availability |
|---|---|---|
| Vssadmin add shadowstorage | Adds a volume shadow copy storage association. | Server only |
| Vssadmin create shadow | Creates a new volume shadow copy. | Server only |
| Vssadmin delete shadows | Deletes volume shadow copies. | Client and Server |
| Vssadmin delete shadowstorage | Deletes volume shadow copy storage associations. | Server only |
| Vssadmin list providers | Lists registered volume shadow copy providers. | Client and Server |
| Vssadmin list shadows | Lists existing volume shadow copies. | Client and Server |
| Vssadmin list shadowstorage | Lists all shadow copy storage associations on the system. | Client and Server |
| Vssadmin list volumes | Lists volumes that are eligible for shadow copies. | Client and Server |
| Vssadmin list writers | Lists all subscribed volume shadow copy writers on the system. | Client and Server |
| Vssadmin resize shadowstorage | Resizes the maximum size for a shadow copy storage association. | Client and Server |
| Source:Microsoft |
2. Ensure that the VSS writers are in Stable State
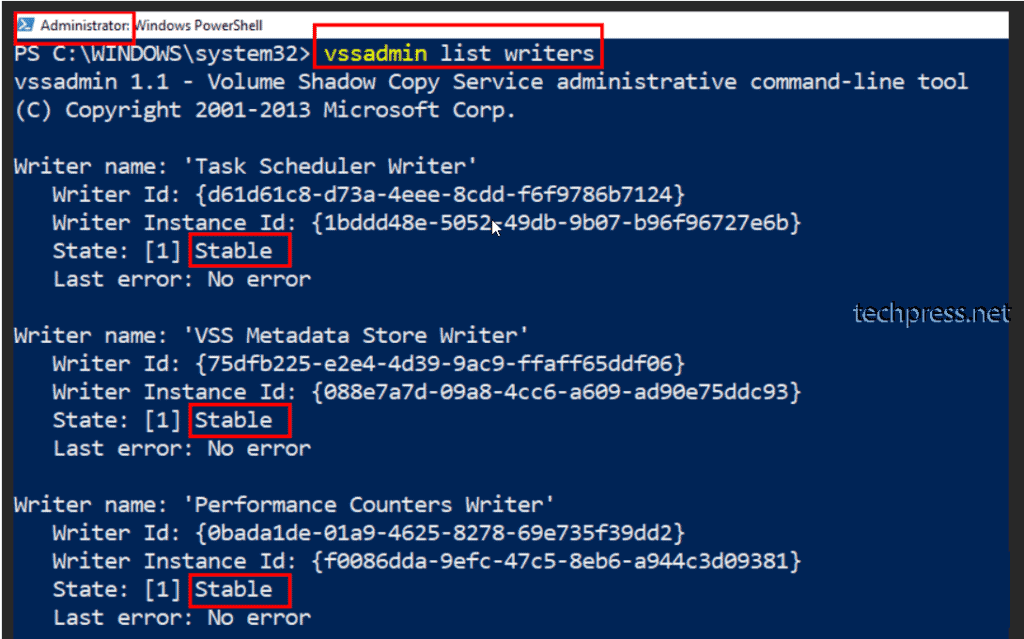
Open command prompt or PowerShell console on the affected server and run vssadmin list writers command to check and confirm if all VSS writers are in a stable state.
Along with generic VSS writers installed on the device, the command will also list application specific writers as well. For example, if you are running this command on an exchange server, it will also list Microsoft Exchange VSS writer along with other generic ones.
Command will output below information on the console.
- Writer name
- Writer Id
- Writer Instance Id
- State
- Last error
If any VSS writer is not in stable state, you can check the error message and fix it by checking the health of the component. For example, If the status of the Microsoft Exchange Writer is not stable, you can restart Microsoft Exchange Information Store Service or reboot the Exchange server. Run vssadmin list writers command again to confirm if the VSS writer is in stable state before triggering a backup.
3. Verify Registered Shadow Copy Providers
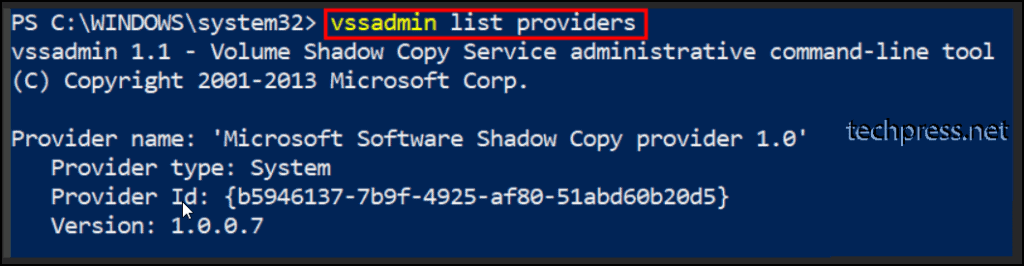
You can list the registered shadow copy provider by running vssadmin list providers command. If you don’t find any shadow copy providers after executing this command, it could indicate issues related to volume shadow copy service (VSS) or the operating system itself.
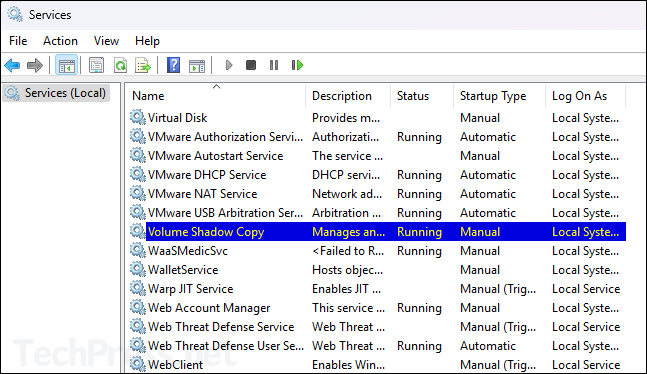
- Press Win + R to open Run dialog box.
- Type
services.mscand press Enter. - Check Volume Shadow Copy service status.
Stop/Start/Restart VSS service using Powershell
Start-Service -Name VSS
stop-Service -Name VSS
restart-Service -Name VSS4. List Existing Volume Shadow Copies
To list all volume shadow copies on the computer, use the command vssadmin list shadows.
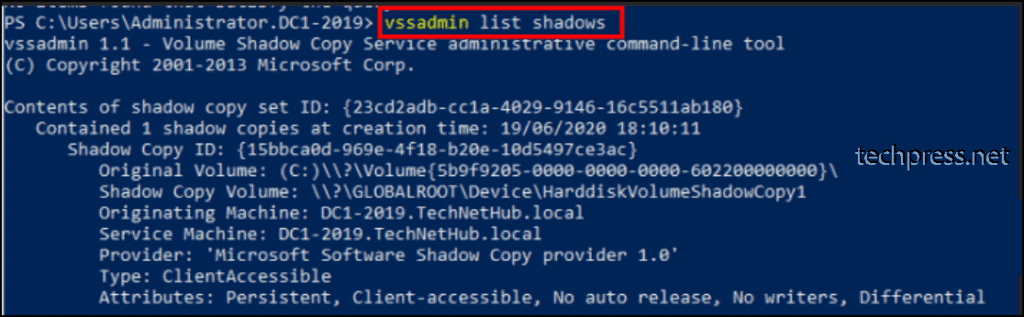
5. Lists all Shadow copy Storage Associations
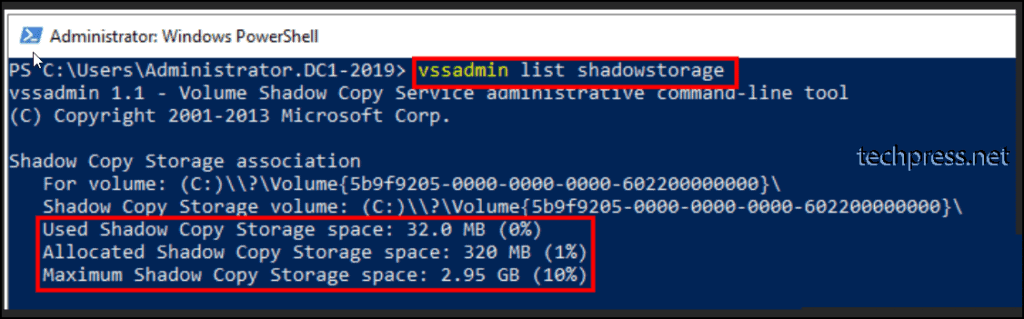
To view all storage associations for existing shadow copies, run the vssadmin list shadowstorage command. By default, 10% of volume storage is allocated to shadow copies.
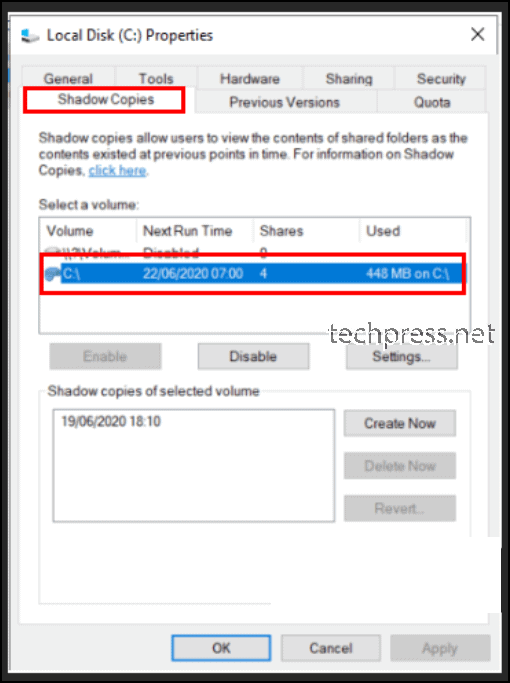
You can also check the Shadow copy storage association on the volume by right-clicking the volume > Properties > Shadow Copies tab.
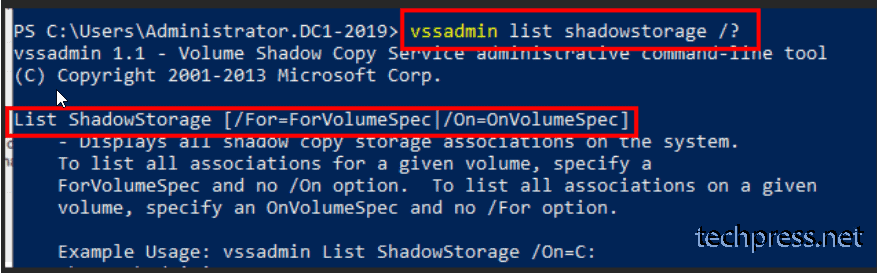
To explore additional parameters for the vssadmin list shadowstorage command, run vssadmin list shadowstorage /?. This will provide you with more options, such as the /for parameter, which allows you to list all associations for a specified volume.
6. Delete Shadow Copies using Command line
You have several options for deleting shadow copies. Shadow copy data is stored in a hidden system folder called System Volume Information. If you notice that this folder is taking up a significant amount of space, you can check for outdated shadow copies that might be stored there and delete it to free up space. To delete shadow copies, use the following commands:
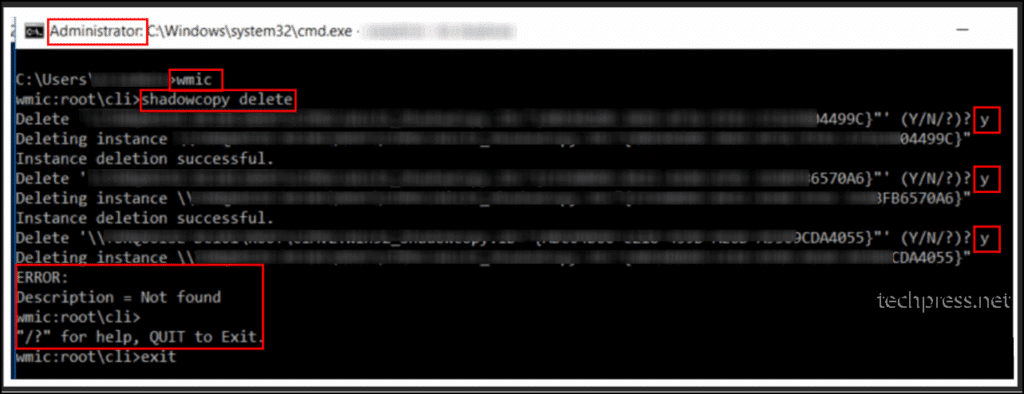
wmic command
Use the wmic command to delete shadow copies. When you run this command, you’ll be at the wmic:\root\cli> prompt. Type shadowcopy delete to delete the shadow copies one by one. Type Y to confirm the deletion of a shadow copy, or N to skip to the next one.
Note: To find the shadow copy ID, use the command vssadmin list shadows. If, after using the wmic command, you find that the shadow copies are not deleted or encounter an error message. You have the option to use either the Vssadmin delete shadows command or the Diskshadow command, as demonstrated in the following sections.
Vssadmin delete shadows
vssadmin delete shadows command allows you to delete either all shadow copies or specific shadow copies from the volume. To see a list of parameters that can be used with this command, add /? at the end of the command and press Enter.
If you wish to delete all shadow copies using the vssadmin delete shadows command, you can use the following command.
Delete all Shadow Copies
Vssadmin delete shadows /alldiskshadow Command
You can also use diskshadow command to delete all the shadow copies from the system. Open the command prompt as administrator > Type diskshadow > then on the DISKSHADOW> prompt type delete shadows all to delete/remove all shadow copies from the server. Diskshadow command reference.

Best Practices
Best practice when configuring Shadow copy is to use a disk that won’t be shadow copied and has sufficient free space to accommodate the shadow copies according to the configuration.
Error code 0x80042302
You may receive this error message during a Windows device backup or system restore:
A Volume Shadow Copy Service component encountered an unexpected error. Check the Application event log for more information.
To resolve this error, follow below troubleshooting steps:
- Press the Windows key + R to open a Run dialog box.
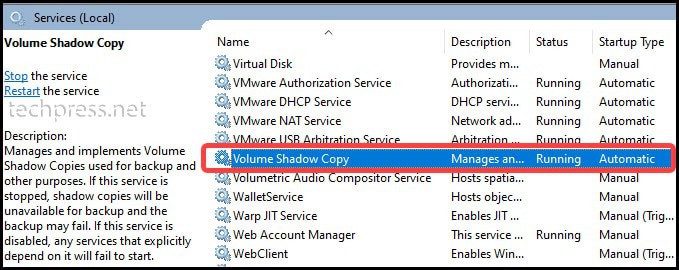
- Type services.msc and press Enter.
- In the list of services, locate the Volume Shadow Copy service.
- Check its Startup Type If it’s disabled, double-click on the service.
- Change the Startup type to Automatic.
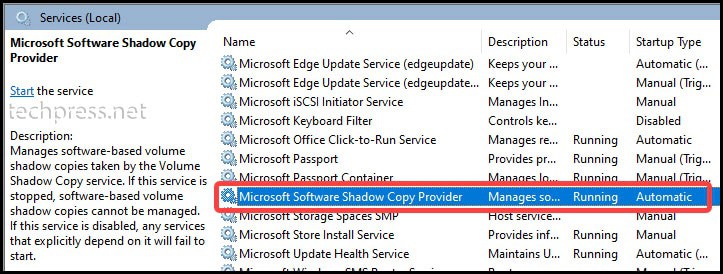
- Ensure that the Microsoft Software Shadow Copy Provider service is not disabled. If it is disabled, you should double-click on the service and set the startup type to Automatic.
- If the error message persists, you can try temporarily disabling Windows Defender and any third-party security systems installed on the device.
- Try to initiate the backup or perform the system restore again to check if the issue is resolved. After completing the backup process, remember to re-enable your security systems and Windows defender.
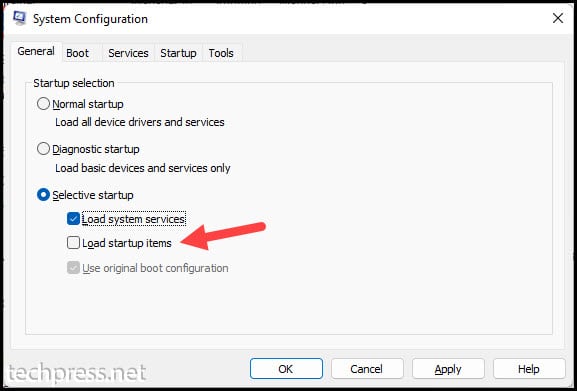
- Perform a Clean boot of your Windows device. To enable a clean boot on the device:
- Press Windows Key + R to open the Run box.
- Type
msconfigin the run box and press Enter. - Go to the General tab and uncheck Load startup items from selective startup.
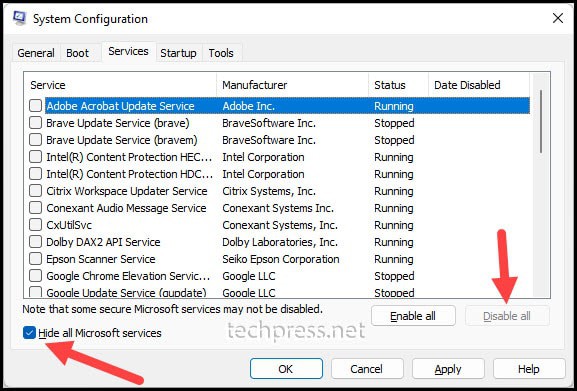
- In the Services tab, choose Hide all Microsoft services and then click the Disable All button located in the bottom right-hand corner of the window.
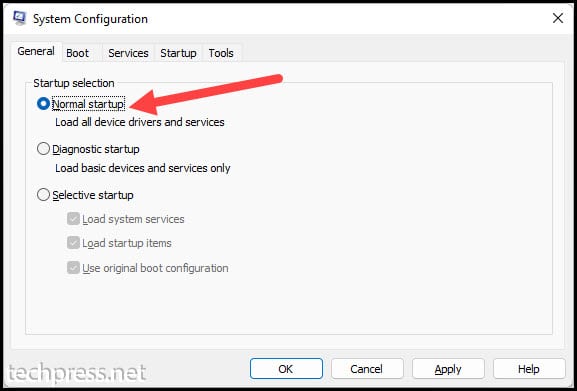
- Click on Apply or OK to save the changes.
- Restart your device.
Test Volume Shadow Copy to ensure it’s functioning correctly. Once the issues are fixed, make sure to change the startup type back to Normal startup.

Thanks so much!!!! WMIC !!!!
No Problem, Livio Mozarth.
Excellent article, thanks!