In this post, I will demonstrate the steps to deploy Santa app on macOS using Intune. What is Santa App? Here’s the official definition, Santa is a high-performance open-source security agent for macOS that provides binary & file-access authorization and rich system event logging.
Think of Santa as Applocker for macOS. It monitors every program launch and, based on rules you define, either allows it or blocks it. Santa has two modes: Monitor (everything runs; events are logged) and Lockdown (default deny; only approved software runs).
Contents
Step1: Download Santa App
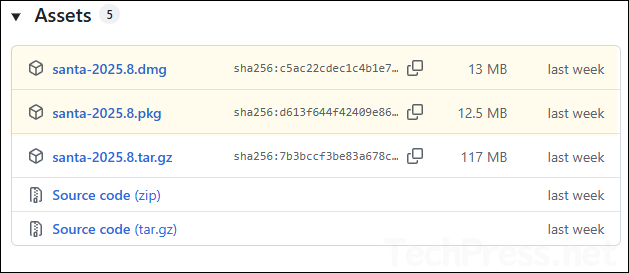
- Go to the northpolesec/santa Releases page. Use the latest version number > Scroll down on the page to find Assets section, where you’ll find DMG and PKG installers. You can use either installer to deploy the app. I’ll download the Santa PKG file. For deploying a DMG installer, refer to the guide: Deploy DMG Apps On MacOS Using Intune.
Step 2: Create Santa App deployment on Intune
Follow below steps to create Santa app deployment on Intune admin center. As I will be using app’s .pkg installer file, I can use either line-of-business (LOB) app or macOS app (PKG) deployment option. I will go with line-of-business app option as I want to deploy this app as a managed app. There are few prerequisites before an app can be deployed as managed using LOB app deployment method. For more information, refer to the link: Difference between Managed and Unmanaged PKG App.
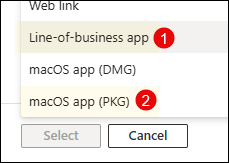
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Apps > macOS > macOS apps. Click on + Create.
- App type: Line-of-business app.
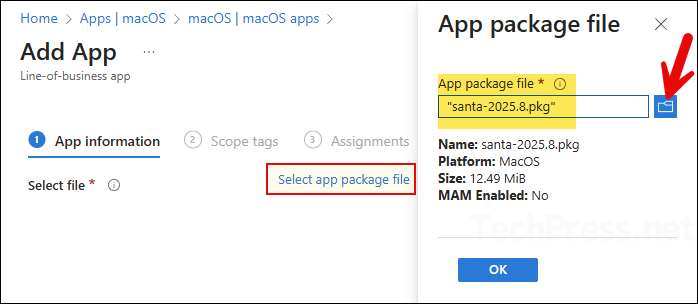
- Click Select app package file and browse to Santa PKG installer file downloaded in the previous step.
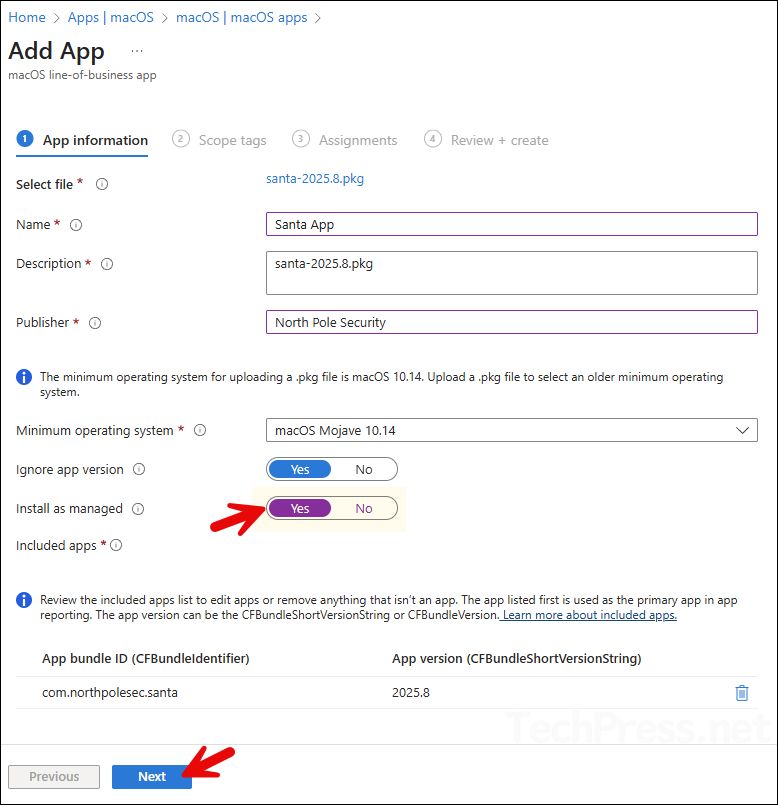
- On the App information tab:
- Provide a name and description of the app.
- Select Minium Operating system.
- Ignore app version: Keep default (Yes).
- Install as managed: change this to Yes.
- App bundle ID and App version information will be pre-populated.
- Rest of the options are optional, but I will suggest filling those out, this helps during troubleshooting app deployment issues.
- Scope tags (optional): A scope tag in Intune is an RBAC label you add to resources (policies, apps, devices) to limit which admins can see and manage them. For more Information, read: How to use Scope tags in Intune.
- Assignments: Assign the app to Entra security groups that contain the target users or devices. As a best practice, pilot with a small set first; once validated, roll it out more broadly. For guidance on assignment strategy, see Intune assignments: User groups vs. Device groups.
- Review + create: Review the deployment summary and click Create.
Monitoring Intune App Deployment
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Apps > All apps.
- Click the app you want to monitor. Check the installation status from Overview page.
- Click Device install status and User install status to see detailed installation status by device and by user for this app.
Sync Intune Policies
The device check-in process might not begin immediately. If you’re testing this policy on a test device, you can manually kickstart Intune sync from the device itself or remotely through the Intune admin center.
Alternatively, you can use PowerShell to force the Intune sync on Windows devices. Restarting the device is another way to trigger the Intune device check-in process.
End User Experience
To check and confirm if the app has been deployed successfully, follow below steps:
- Sign in to one of the target Mac device
- Go to Finder > Go > Applications and look for the Santa app icon to confirm the deployment.
macOS Intune Deployment Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues deploying the app, investigate using IntuneMDMDaemon*.log and IntuneMDMAgent*.log files. For help locating these logs files on a macOS device, refer to the link: Collect Intune Logs From a macOS Device.
