In this post, I will show you how to deploy Android studio on macOS with Intune. Android Studio is Google’s official IDE for building Android apps, bundling a Kotlin and Java code editor, visual layout tools, the Android SDK, Gradle, an emulator, and debugging and profiling tools; on a Mac it lets you create, run, test, and publish Android apps on Apple Silicon or Intel using Apple’s Hypervisor for fast emulators.
Contents
Download Android Studio DMG Installer
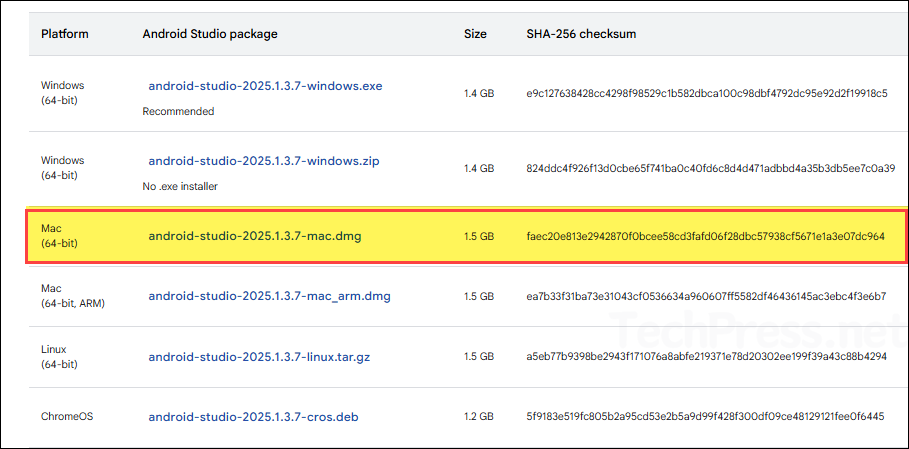
- Visit the website https://developer.android.com/studio and scroll down on the page to find the section Android Studio downloads. The installers are listed with their platform information. Select the DMG installer to start the download process. Please note that there is a separate DMG installer for ARM processor devices. Use that if you are deploying it on ARM devices.
Create Intune Deployment for Android Studio
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Apps > macOS > macOS apps > Click + Create.
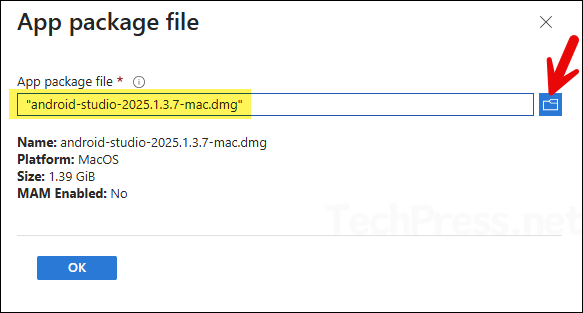
- App type: macOS app (DMG) > Click Select.
- Browse to the downloaded DMG installer file and click OK.
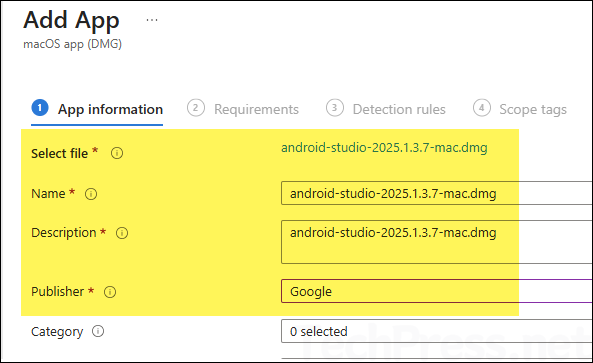
- App Information: Provide a name, description, and Publisher information.
Apart from the Name, Description, and Publisher, providing additional information is optional. However, including the rest of the details can help other team members in troubleshooting issues and also serve as app documentation.
- Requirements: Select Minimum operating system as a condition for application installation. Click on Next to proceed.
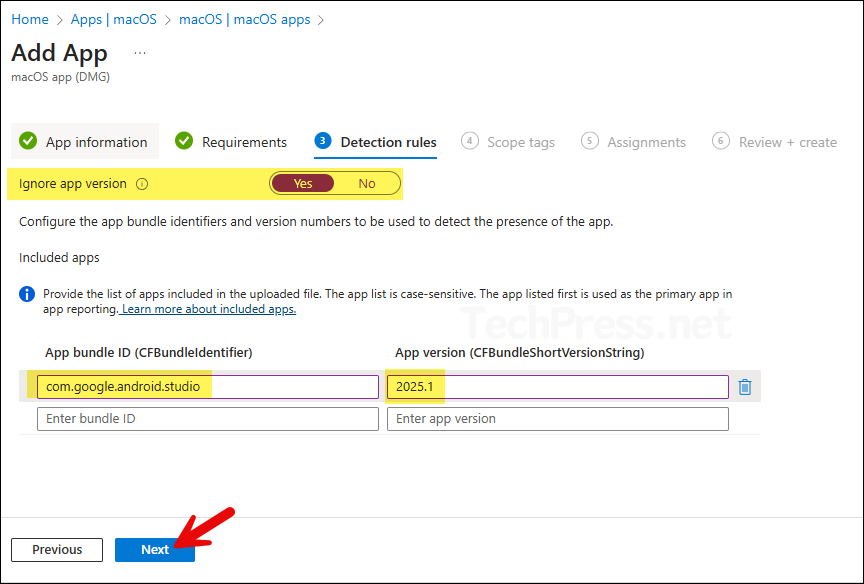
- Detection rules:
- If you select Ignore app version = Yes, Intune will detect the app by bundle ID only and therefore won’t keep trying to reinstall or mark it as not detected. Intune will check for the app, if it’s not found on the device, it will install it. If the app is installed, but its version number is different, it will ignore the version and do not try to reinstall the app.
- If you select Ignore app version = No, then the app will be installed if it’s not found on the device. If you have updated the app and now the version number is different from what is in the Intune deployment package, Intune may try to reinstall the app.
In general, when deploying a self-updating application such as Google Chrome or Zoom, you should set Ignore app version to Yes. Android Studio has its own built-in updater and tends to update frequently, therefore set Ignore app version to Yes.
In some cases, you may choose to disable the autoupdating setting for an app to manage app updates only from Intune, then you can select Ignore app version to No.
Note
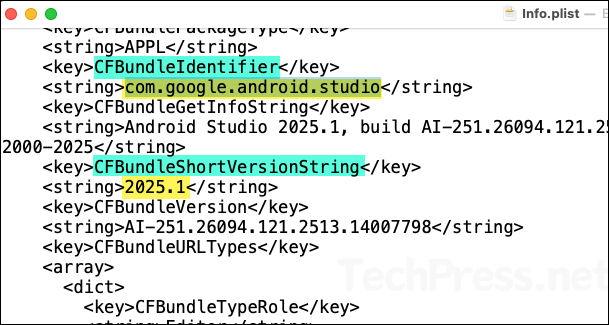
In the Included apps section, provide the App bundle ID (CFBundleIdentifier) and the App version (CFBundleShortVersionString) information. To retrieve these details, Install the Android Studio DMG file (the same one you intend to deploy via Intune) on a test Mac device and then use the following commands in the macOS terminal to obtain this information:
CFBundleIdentifier
defaults read "$HOME/Applications/Android Studio.app/Contents/Info" CFBundleIdentifier
CFBundleShortVersionString
defaults read "$HOME/Applications/Android Studio.app/Contents/Info" CFBundleShortVersionString

Alternatively, you can also get CFBundleIdentifier and CFBundleShortVersionString information from Info.plist file.
- Go to Finder > Go > Go to Folder.
- Type this path /Applications/Android Studio.app/Contents/ and press Enter.
- You Wil find Info.plist file in the Contents folder.
- Double-click on the file and search for
CFBundleIdentifierandCFBundleShortVersionStringvalues.
- Once you’ve collected all the required information, enter it in the Detection Rules tab, click Next.
- Scope tags (optional): A scope tag in Intune is an RBAC label you add to resources (policies, apps, devices) to limit which admins can see and manage them. For more Information, read: How to use Scope tags in Intune.
- Assignments: Assign the app to Entra security groups that contain the target users or devices. As a best practice, pilot with a small set first; once validated, roll it out more broadly. For guidance on assignment strategy, see Intune assignments: User groups vs. Device groups.
- Review + create: Review the deployment summary and click Create.
Sync Intune Policies
The device check-in process might not begin immediately. If you’re testing this policy on a test device, you can manually kickstart Intune sync from the device itself or remotely through the Intune admin center.
Alternatively, you can use PowerShell to force the Intune sync on Windows devices. Restarting the device is another way to trigger the Intune device check-in process.
Monitoring Intune App Deployment
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Apps > All apps.
- Click the app you want to monitor. Its Overview page shows the app’s install status.
- Click Device install status and User install status to see detailed installation status by device and by user for this app.
End User Experience
Once you create the Intune deployment and the devices have checked in, Android Studio will install on the target Macs. It is a large application, so installation can take some time. Allow at least 15 to 20 minutes after check-in for the app to complete installation. Once the app installation is complete, you can verify it using below steps:
- Go to Finder > Go > Applications
- Look for the Android Studio icon to confirm the deployment.

Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues deploying the app, investigate using IntuneMDMDaemon*.log and IntuneMDMAgent*.log files. For help locating these logs files on a macOS device, refer to the link: Collect Intune Logs From a macOS Device.
